Hexagon Flange Bolt ISO 4162
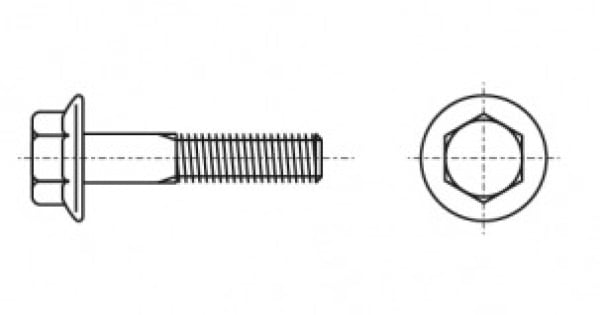
The hexagon flange bolt ISO 4162 is a versatile fastening element widely used across various industries. Its distinguishing feature is the presence of a flange beneath the head, which provides an increased bearing surface. This allows for a more uniform distribution of load on the fastened part. Thanks to the hexagonal head, the bolt can be conveniently tightened and loosened using standard wrenches, making it practical for use.
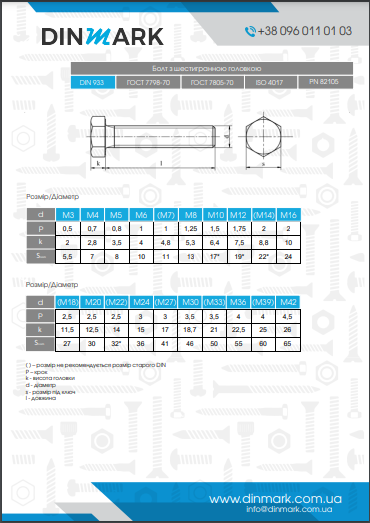
Technical Specifications of ISO 4162
The hexagon flange bolt ISO 4162 is a standardized fastening element with an integrated flange under the head. This flange ensures even load distribution, enhancing connection reliability and eliminating the need for additional washers. The hex head allows for convenient tightening and loosening using standard tools.
Key Characteristics:
-
Shape: The bolt consists of a cylindrical shaft with external threading, a hexagonal head, and an integrated flange beneath the head. The flange acts as an extended base that contacts the surface of the part, evenly distributing axial loads.
-
Material: Made from carbon steel for high strength or stainless steel (A2, A4) for corrosion resistance.
-
Coating: To protect against corrosion and improve performance, the bolts may have different coatings such as zinc (electroplated or hot-dip), phosphate, or black oxide.
ISO 4162 Strength Classes
The strength class of a bolt reflects its mechanical properties, particularly its ability to withstand loads without permanent deformation or failure. For ISO 4162 bolts, as with other metric bolts, the strength class is denoted by two numbers separated by a dot.
-
The first number (e.g., 8 in 8.8) represents one hundredth of the nominal tensile strength (Rm) in N/mm² (or MPa). For example, class 8.8 has a tensile strength of 8×100 = 800 N/mm².
-
The second number (e.g., 8 after the dot in 8.8) represents one tenth of the ratio of the yield strength (Rp0.2) to the tensile strength. So, for class 8.8, the yield strength is 0.8×800 = 640 N/mm² — the stress at which the material begins to plastically deform.
Most Common Strength Classes:
-
Class 8.8: High-strength bolts for general industrial and mechanical applications, capable of withstanding significant static and dynamic loads.
-
Class 10.9: Higher strength bolts used in heavy engineering, bridge construction, and automotive applications for highly stressed joints.
-
Class 12.9: The highest standard class for bolts, used in critical applications requiring maximum load-bearing capacity and resistance to extreme loads, such as precision mechanisms or components exposed to high cyclic stresses.
The selection of the appropriate strength class is crucial and depends on calculated loads, operating conditions, and structural safety requirements.
Fastener Group: Hexagon Flange Bolt ISO 4162
ISO 4162 bolts belong to the metric fastener group, as their dimensions and specifications are precisely defined by international standards. Depending on the material and strength class, they can also be categorized as follows:
-
High-strength fasteners: Includes bolts with strength classes 8.8, 10.9, and 12.9, designed for heavily loaded joints. Their use can reduce the number of fasteners needed or allow for more compact and lightweight constructions without compromising strength.
-
General-purpose industrial fasteners: Bolts made of carbon steel without specific high-strength requirements. These are suitable for most standard applications across various industries.
-
Stainless steel fasteners: Bolts made from stainless steels (A2, A4) that offer high corrosion resistance and are ideal for damp, aggressive, or chemically active environments where regular steel bolts would quickly corrode.
ISO 4162 Materials
Materials used for manufacturing ISO 4162 bolts are selected based on the required strength, corrosion resistance, and operating conditions.
Main materials:
-
Carbon steel
-
Stainless steel (A2, A4)
Application Areas of ISO 4162
Hexagon flange bolts ISO 4162 are versatile fasteners widely used in various industries and construction due to their reliability and ability to evenly distribute load. The flange design eliminates the need for extra washers, simplifying installation and saving time.
Key Application Areas:
-
Mechanical Engineering: Used in the assembly of various machines, tools, and equipment requiring strong, reliable connections. The flange helps prevent surface damage during tightening and enhances vibration resistance.
-
Automotive Industry: Found in vehicles, motorcycles, buses, trucks, and agricultural machinery. Used in critical joints such as engines, transmissions, suspensions, and chassis components where vibration and dynamic load resistance are essential.
-
Construction: Widely used in assembling metal structures, building frames, bridges, supports, and other load-bearing components that require high strength and long-lasting connections.
-
Steel Structures Manufacturing: Suitable for joining profiles, beams, and other metal components in industrial and civil structures where strong and durable joints are needed.
-
Energy Sector: Used in power plant equipment (thermal, hydro, nuclear, wind), transformer substations, and other installations requiring reliable fastening under significant temperature and mechanical loads.
-
General Industrial Use: Applicable in various industrial and household scenarios where a fastener with increased bearing area is needed to prevent surface damage and ensure a secure joint.
-
Marine and Shipbuilding Industry: Stainless steel (A4) bolts are preferred in these fields due to their excellent corrosion resistance in aggressive marine environments.