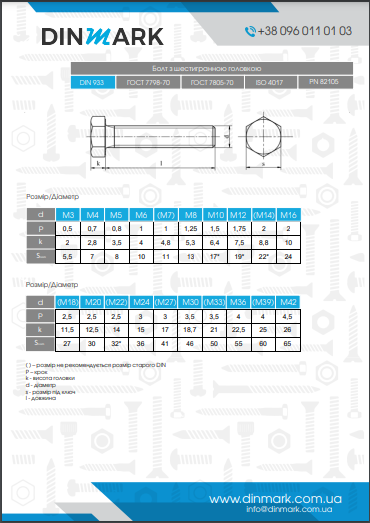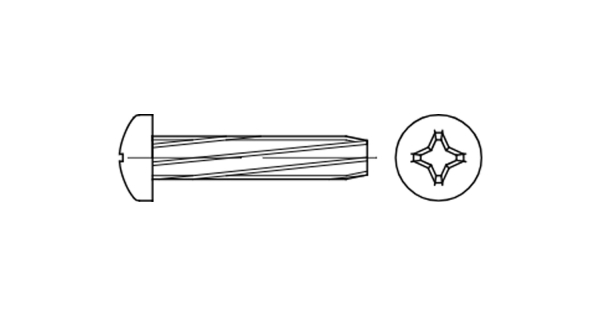
DIN 7516 A Self-Tapping Screw with a Round Head
Technical Characteristics of DIN 7516 A
DIN 7516 A is a self-tapping screw with a round head designed for creating secure connections in metal without pre-cutting threads. The key feature of this screw is its specially designed thread, which allows it to form a threaded connection independently in a hole.
Main characteristics:
- Head type: round, with a slotted or Phillips drive
- Thread: self-tapping, enabling strong connections without additional thread-cutting tools
- Material: carbon steel or stainless steel
- Coating: zinc-plated, nickel-plated, or phosphate-coated for corrosion protection
- Purpose: fastening metal components, assembly of structures, securing casing elements
DIN 7516 A screws are widely used in industry, automotive manufacturing, and construction due to their high reliability and ease of use.
Strength Class of DIN 7516 A Self-Tapping Screw with a Round Head
The strength class of this type of fastener depends on the material used. The main strength grades include:
- Carbon steel grades 4.8, 5.8, 8.8 – provide sufficient strength for standard loads.
- Stainless steel A2, A4 – high corrosion resistance, allowing use in high-humidity conditions.
- Zinc-plated steel – coating protects the screw from corrosion, extending its service life.
The choice of strength class depends on the operating conditions and the required load-bearing capacity of the fastener.
Fastener Group of DIN 7516 A
DIN 7516 A belongs to the group of self-tapping screws, which are used to create connections in metal without pre-cutting threads in the hole. They ensure reliable fastening due to the special thread design, which independently forms a mating thread in the material.
This type of screw is commonly used where quick fastening is required without the need for additional threading tools.
Manufacturing Materials of DIN 7516 A Self-Tapping Screw with a Round Head
DIN 7516 A screws are made from various materials depending on operating conditions and required strength levels:
- Carbon steel – the most common option, providing good mechanical strength.
- Stainless steel (A2, A4) – used in high-humidity and aggressive environments, does not require additional coating.
- Zinc-plated steel – coating protects against corrosion, allowing screws to be used in humid environments.
The choice of material depends on the application. Carbon steel is sufficient for standard constructions, while stainless steel is preferable for humid or corrosive environments.