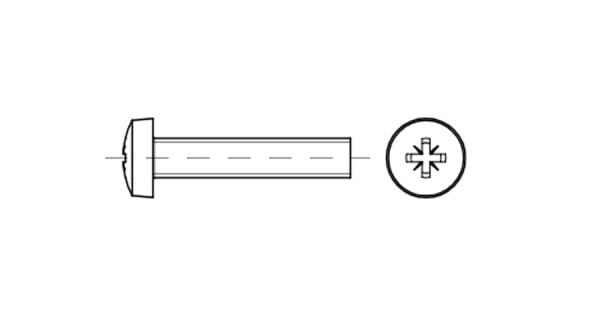
DIN 85 is a type of fastener that looks like an ordinary metal rod with a torque-transmitting head at one end and an external thread at the other end. The advantage of this screw is its versatility - it provides a secure connection with a tight fit of the head. To use the fastener, you need to prepare the hole and cut the thread, after which you can make the connection using a standard screwdriver.
Strength class DIN 85
DIN 85 screws are made of steel with a strength class of 4.8.
DIN 85 fastening group
Depending on the material of manufacture, DIN 85 screws are divided into groups:
- Stainless steel fasteners
- Brass fasteners
- Polyamide fasteners
Materials for the manufacture of DIN 85 screws
DIN 85 screws are made of the following materials:
- Steel with a strength class of 4.8, which can optionally be plated with zinc. Plated zinc protects against corrosion if the fastener is to be used in aggressive environments.
- Stainless steel grades A2 and A4. It allows the fasteners to be used at significant temperature changes and in aggressive and humid environments.
- Brass. Brass screws are used when the system is subjected to frequent dynamic, vibration, and cyclic loads.
- Polyamide. Polyamide screws can withstand mechanical shocks, do not crack or break at the permissible load factor.
Scope of use of DIN 85 screws
This type of hardware is designed to form a fastening assembly in the form of screwing into a threaded hole or fastening several elements by adding washers and nuts. A standard straight screwdriver or a power tool equipped with appropriate bits is used to screw hardware.
DIN 85 is widely used in mechanical engineering, aircraft construction, instrumentation, and furniture production.