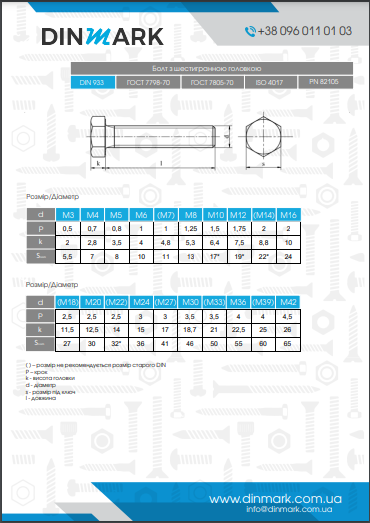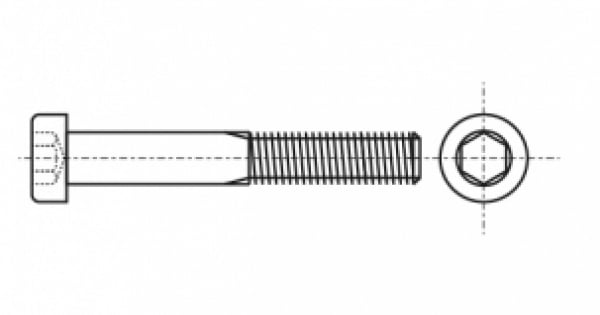
According to DIN 912, it is manufactured with a full metric thread and a cylindrical head. This type of fastener is considered universal and is widely used for reliable threaded connections in wood, metal, plastic and other materials. The head of the bolt also has an internal hexagon and can be easily tightened with a special tool with a high tightening force.
Strength class DIN 912
The strength class of a bolt is the maximum applied force at which the bolt begins to fracture. Bolts are manufactured in strength classes from 8.8 to 12.9. From class 8.8, a bolt is considered high-strength.
High-strength bolts are made of alloy steel and are used in critical projects where, in addition to high static loads, the bolt is subjected to constant vibration.
Fastening group DIN 912
Depending on the material of manufacture, the bolt is divided into different fastening groups:
- High-strength fasteners
- Stainless steel fasteners
Materials of manufacture
The bolt is available in the following materials:
- Steel, which can optionally be coated with hot-dip, plate, plain, yellow and plate black zinc
- Stainless steel (A2, A4) does not need to be coated
Where stainless steel bolts DIN 912 are used
They are used in a variety of industries: Construction, industry, instrumentation, and automotive. High-strength fasteners are also used in the national economy: in hazardous environments, at high and low temperatures, with strict requirements for withstanding high tensile forces under high static and dynamic loads.
In addition, the scope of application directly depends on the material of manufacture and coating of the product:
- Galvanized steel provides good corrosion protection if the fastener is to be used in aggressive environments.
- Stainless steel allows the fasteners to be used at high temperature extremes and in aggressive and humid environments.