DIN 558 full thread bolt is one of the most commonly used fasteners in various industries, especially popular in mechanical engineering and instrumentation, where they are used to fasten massive parts of metal structures.
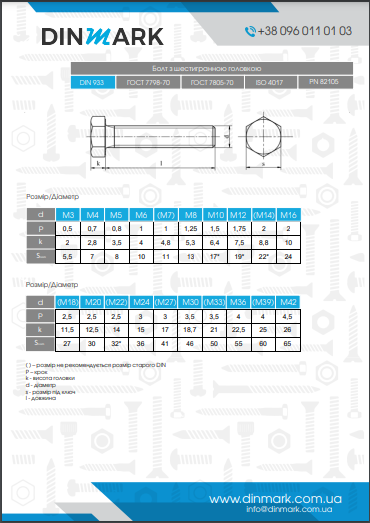
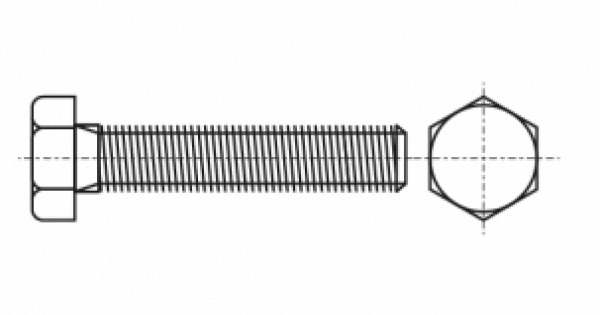
Hexagonal bolt DIN 558 is a rod with a thread (metric or inch) along its entire length and a hexagonal head. In some cases, the bolt may have a straight spline. It is used in conjunction with nuts and washers of the appropriate size.
Strength class DIN 558
The strength class of a DIN 558 bolt is the maximum applied force at which the bolt begins to fracture. DIN 558 bolts are available in strength classes from 5.8 to 12.9. From strength class 8.8, the bolt is considered high-strength.
High-strength DIN 558 should be purchased only from trusted suppliers. It is made of alloy steel and such bolts are used for critical projects where, in addition to high loads and static loads, the DIN 558 bolt is subjected to constant vibration. Such bolts will be especially relevant in bridge construction, instrumentation, and in structures that are located near objects subject to vibration.
Stainless steel bolt DIN 558 also has its own strength classes:
- 50 - mild steel (500 MPa)
- 70 - cold-formed steel (700 MPa)
- 80 - high-strength steel (800 MPa)
Fastening group DIN 558
Depending on the material of manufacture, the DIN 558 hexagonal head bolt is divided into different fastening groups:
- High-strength fasteners - fasteners made of steel with a strength class of 8.8 or higher.
- Brass fasteners - fasteners made of brass.
- Stainless steel fasteners - fasteners made of stainless steel.
- Polyamide fastener - fastener made of polyamide
Bolt materials according to DIN 558
The technical characteristics of a full-threaded bolt also directly depend on the material of the bolt.
The DIN 558 bolt is made of:
1. Steel. The range of strength class of this material is 5.8-12.9. In addition, this material can be additionally coated:
- Zinc for better corrosion protection if the product is to be used in aggressive environments.
- Dacromet, this type of coating does not lead to hydrogen embrittlement on steel. It also has electrically conductive properties; its more electronegative potential in relation to steel creates electrochemical protection in addition to barrier protection.
- Zinc plate - it has similar properties to ordinary zinc, but the bolt looks matte.
- Yellow zinc - similar properties to regular zinc, but the color of the bolt is different - yellow.
- Hot-dip galvanized - products with this coating are the most resistant to corrosion.
2. Stainless steel A2, A4, A5. Allows the fasteners to be used at significant temperature changes and in aggressive and humid environments. Also, this material does not require additional coating.
3. Brass. Brass bolts are used if the system is subjected to frequent dynamic, vibration and cyclic loads.
Areas of application for DIN 558 bolts
The DIN 558 bolt is used in bolted and screwed connections in construction, mechanical engineering, industrial and manufacturing areas with washers and nuts of appropriate sizes. It is also frequently used with anchor sleeves and driven anchors.
The application of DIN 558 also depends on the material of its manufacture:
- Steel, cold-dip galvanized, Galvanized bolts are used in the operation of industrial production facilities.
- Hot-dip galvanized steel - construction and installation work, both external and internal.
- Brass - structures with increased requirements for decorative characteristics, electrical appliances, plumbing fixtures.
- Stainless steel - A4 - food industry; A2 - coastal structures and facilities.
- High-strength steel - construction of multi-storey buildings, road structures, bridges and subways.