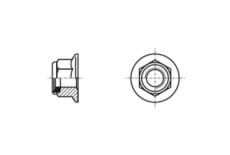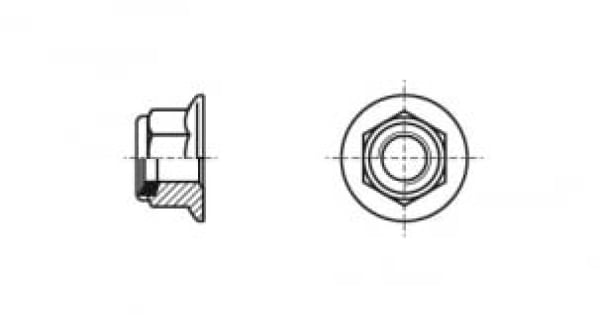
DIN 6926 A flange nut is a fastener that creates a detachable threaded connection with an increased contact area, which allows for both redistribution of pressure on the material and a larger friction area to prevent loosening and is used when fastening parts to grooves along which the part can move. DIN 6926 has a polyamide ring in its design, which makes it self-contracting.
Strength class of DIN 6926
The strength class of a Din 6926 nut is the maximum applied force at which the nut begins to fracture. Din 6926 nuts are manufactured in strength classes 8 and 10. From strength class 8, the nut is considered high-strength. High-strength Din 6926 should be purchased only from trusted suppliers. It is made of alloy steel and such nuts are used for critical projects where, in addition to high loads and static loads, the din 6926 nut is subjected to constant vibration.
DIN 6926 fastening group
Depending on the material of manufacture, DIN 6926 nuts are divided into groups:
- Stainless fasteners - fasteners made of stainless steel
- High-strength fasteners - fasteners made of steel of strength classes 8 and 10.
Materials for the manufacture of DIN 6926 nuts
DIN 6926 nuts are made of the following materials:
- High-strength structural alloy steel of strength classes 8 and 10. The high strength class allows the nuts to be used in highly loaded connections. Which can be additionally coated:
- Zinc protects against corrosion if the fasteners are to be used in aggressive environments.
- Zinc plating protects against corrosion if the fasteners are to be used in aggressive environments.
- Delta-Mks - zinc dispersed anti-corrosion coating systems. They outperform all traditional types of coatings in terms of corrosion resistance. Increase the service life of fasteners in urban environments by 5 times.
- Stainless steel grades A2 and A4
Areas of application for DIN 6926 nuts
The DIN 6926 nut is used in production where there is a slightly acidic environment, such as shipbuilding and the space industry. Hexagonal nuts DIN 6926 are most often used in high-strength connections.