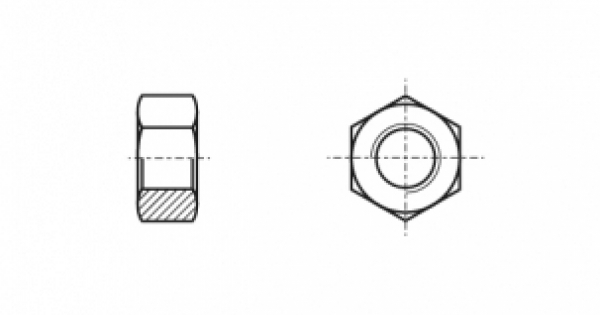
ISO 4032 What is it? ISO 4032 (Din 934) is the most common nut that has a hexagonal shape. This nut is used to create high-strength detachable connections of metal parts and is used in conjunction with bolts and screws. The ISO 4032 nut has six faces with a thread (metric or inch) on the inside. To fasten ISO 4032 nuts, use wrenches of the appropriate size.
Strength class ISO 4032
ISO 4032 nuts are manufactured in strength classes 5, 6, 8, 10, 12. A strength class is a 100-fold reduction in the minimum strength of a bolt that can be paired with a metal product to withstand normal loads. That is, even the minimum strength class of an ISO 4032 nut can withstand more than 500 MPa.
Fastening group ISO 4032
Depending on the material of manufacture, ISO 4032 nuts are divided into:
- High-strength fasteners
- Stainless steel fasteners
- Polyamide fasteners
- Brass fasteners
- Copper fasteners
- Aluminum fastener
Materials of manufacture of the nut ISO 4032
The ISO 4032 nut is widely used in construction equipment: bulldozers, cranes, excavators; power and industrial units: turbines, pumps, power generators, metalworking machines; trucks and agricultural machinery: trailers, semi-trailers, tractors, tractors.
ISO 4032 nuts are used in conjunction with bolts or screws to create a secure threaded connection.
The scope of application also directly depends on the material of the nut:
- Galvanized steel offers good corrosion protection if the fastener is to be used in an aggressive environment.
- Brass is used if the system is subjected to frequent dynamic, vibration loads.
- Stainless steel allows the fasteners to be used at significant temperature changes and in aggressive and humid environments.
- Polyamide withstands mechanical shocks, does not crack or break at the permissible load factor.
- Copper is resistant to corrosion in dry air, fresh and salt water, alkaline solutions, organic acids, alcohols, and phenolic resins.
- Aluminum, due to the deformation of mild steel, seals the joint well.