Bolts are one of the most common fasteners used in various fields of activity. They are used in construction, mechanical engineering, shipbuilding, aviation industry and even in everyday life. The main advantage of the bolt connection is its reliability, strength and the possibility of multiple disassembly and assembly. This hardware consists of two main parts: a threaded rod and a head, which most often has a hexagonal shape. Their main purpose is to ensure a reliable connection of parts that can withstand mechanical loads and the influence of the external environment. The variety of types, sizes and characteristics of bolts is impressive, which allows you to choose the best option for each specific task.
Advantages of using: Reliability: Bolts provide a strong connection that can withstand significant loads. Ease of installation: Easy to install and remove with tools. Versatility: Used in various industries, from construction to high-tech products. Durability: They are made of durable materials, which ensures a long service life.
Basic ways of classifying bolts
Shape and dimensions of the head
These parameters bolts are determined by their operating conditions and purpose. The heads can have different configurations, such as hexagonal, cylindrical semi-circular, oval or square. Each of these forms has its own advantages and uses.
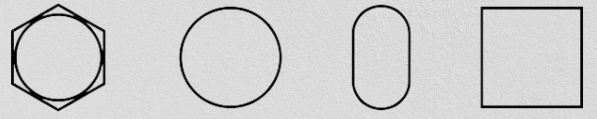
Fig. 1. Top view of the bolt head
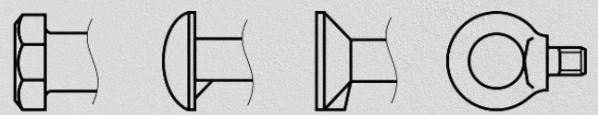
Fig. 2. View from the side of the bolt head
Shape of the rod
These fasteners differ in the shape of the rod: they can have a rod of the same diameter or a stepped rod, as in the prizon versions. In which the diameter of the smooth part of the rod is much larger than the nominal diameter of the thread.
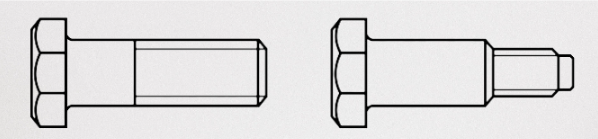
Rice. 3 The shape of the shaft of the bolts
Thread pitch and type
Bolt threads, as an important fastener, are divided into two main categories: metric and inch.
Metric thread: This is the most common type of thread, where dimensions are measured in millimeters. Metric threads are formed by cutting or knurling. Metric threads, denoted by the letter "M", are divided into: threads with a large pitch (standard pitch) and threads with a small pitch. Hexagonal - can have both a normal and a small thread pitch. For each diameter, the standard provides a certain small a step. Half-round and countersunk heads are usually made with a normal thread pitch.
*Examples: hexagon bolts M8 (GOST 7805-70) have a large thread pitch of 1.25 mm and a small pitch of 1.0 mm. M72 bolts (GOST 10602-94) can have a small thread pitch of 4.0 or 6.0 mm. Small thread pitch is used in threaded connections of strength class 8.8 and higher.
Inch thread: This type of threading, where dimensions are measured in inches, is less common but is still used in some industries, especially in appliances manufactured to US standards.
Carving step is the distance between the vertices of adjacent threads. The choice of threading step depends on the purpose of the product and its operating conditions. The correct choice of thread pitch is very important for high-quality connection of parts.
Execution option
Most bolts have different versions, which are design features provided by standards such as GOST or DIN. These options allow you to adapt them to different operating conditions and requirements.
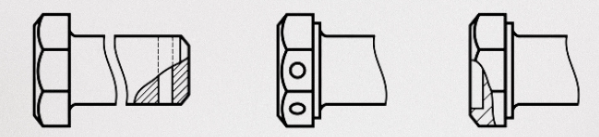
Fig. 4 Variants of execution of bolts
For example, for hexagonal products, there are versions that provide for the possibility of locking the threaded connection. For this, holes for a cotter pin or knitting wire can be made at the end of the threaded part or in the head of the product. This prevents spontaneous unwinding of the hardware during operation.
Another option is a lightweight head, which allows you to reduce the weight of the fastener without changing the turnkey size. For this, a recess is made in the head, which reduces the mass without losing strength and functionality. Such bolts are particularly useful in structures where weight is important, such as in the aviation and automotive industries.
Accuracy class
The accuracy class determines the tolerances and deviations of the thread dimensions, which affects the compatibility of the parts during the connection. The strength, wear resistance and reliability of the fastening depend on the accuracy class.
Metric thread accuracy classes
In metric threads, a system of numerical and letter designations is used:
Number (4, 6, 8, etc.) indicates the tolerance - the smaller the number, the more accurately the thread is made.
Letter (h, H, g) denotes the tolerance direction: H/h – holes and external threads without additional clearance, standard for bolts and nuts. G/g – external thread with a guaranteed gap (for special connections). Js – neutral tolerance, used in precise connections.
Typical accuracy classes for threads:
4H/4h, 5H/5h - very high accuracy, used in aviation, instrument making.
6H/6g – standard accuracy class for mechanical engineering and general application.
7H/7g, 8H/8g – with a large tolerance, used in rough connections, for example, in structural elements.
Inch thread accuracy classes (UNC, UNF, UNEF)
There are three main classes in the inch system:
1A/1B – rough thread, used in connections that require easy installation (for example, in temporary fasteners).
2A/2B – standard accuracy that provides a balance between ease of assembly and reliability.
3A/3B – precise threading for high-load and precision connections (in military and aviation equipment).
Accuracy classes of special threads
In addition to metric and inch threads, there are other types that also have their own accuracy classes:
Trapezoidal carving – usually has tolerances of medium accuracy, as it is used in moving mechanisms (screw gears, elevators).
Conical thread – has special tolerances to ensure tightness. An important characteristic is the taper angle, for example, in pipe connections (BSPT, NPT).
Self-locking thread – its accuracy is regulated by a special profile or coating that prevents self-unscrewing.
There is also a classification of accuracy classes based on DSTU ISO 4759-1, which regulates tolerances for fasteners. It also meets the international standard ISO 4759-1, which defines three main accuracy classes:
Class C – rough connection, the hole diameter is larger by 2-3 mm. It is used in low-responsibility structures, easily mounted, compensates for errors.
Class B – standard precision, the hole is larger by 1-1.5 mm. The most common class, provides a balance between reliability and ease of installation.
Class A – high accuracy, the difference in diameters is 0.25-0.30 mm. It is used in critical connections, requires precise manufacturing of holes, is more expensive to manufacture.
Strength class
Bolts are made of different strength classes and grades of steel, depending on their purpose and field of application. Bolt strength class is indicated on the top of the head and can be normal (4.8, 5.8, 6.8) or increased (8.8, 10.9, 12.9). This marking helps to quickly determine the mechanical properties. Traditionally, markings can be convex or recessed, depending on the method of application.
Strength classes determine their mechanical properties and ability to withstand loads. Each strength class consists of two numbers that have the following values:
First number: Determines the ultimate tensile strength. Multiplied by 100, it indicates the nominal temporary resistance in N/mm². For example, for strength class 10.9, the first number means that the tensile strength limit is at least 1000 N/mm². If the load on the bolt is equal to or exceeds this value, the fastener breaks.
Second number: Multiplied by 10, it indicates the ratio of the minimum yield strength (the stress at which plastic deformation begins) to the strength limit. For example, for strength class 10.9, the second number means that the minimum yield strength is 10 × 9 × 10 = 900 N/mm².
Materials for making bolts
The choice of material is determined by requirements for corrosion resistance, temperature resistance, the ability to work under pressure, in aggressive environments, as well as the presence or absence of certain magnetic properties.
In some cases, when fasteners have high requirements regarding corrosion resistance, mass, strength, dimensions, high heat resistance, absence of sparks upon impact and other characteristics, other metals and alloys are used for their manufacture. It can be brass, titanium, tantalum, beryllium alloys, aluminum, tungsten and others.
The main materials for production are the following:
Ordinary steels: st3, st3kp.
Quality structural carbon steels: 10, 10kp, 20, 20kp, 35, 40, 45.
Alloyed carbon steels: 40H, 20HGSA, 25HGSA, 30HGSA, 35HGSA, 40HGSA.
Low-alloy steels for welded structures: 09G2S.
Corrosion-resistant stainless steels: 10Х17Н13М2Т, AISI 316.
Stainless heat-resistant steels: 08H18N10, 08H18N10T, 12H18N10T, 20H13, 30H13, 40H13, AISI 304.
Heat-resistant relaxation-resistant steels: 25H1MF, 25H2M1F, 30HMA.
Brass: L63.
Copper: MT (wire).
Titanium: VT1-0.
Titanium deformed alloy: VT5.
Nylon (PA6, PA66): it is a polymer material characterized by strength, corrosion resistance, low weight and electrical insulating properties.
H3 Classification by protective coating
To protect against corrosion and improve operational characteristics, bolts can have different protective coatings:
- Galvanized (electrolytic, hot-dip galvanizing)
- Phosphating
- Cadmus
- Nickel plated
- Chromed
- Oxidized (blackened)
Classification by tightening torque
Tightening torque is a torque used to tighten hardware with a certain effort. It depends on:
- Diameter and strength class
- Material and coating
- Presence of lubricant
- Connection type
The exact values of the tightening moments are indicated in the relevant standards (GOST, DIN, ISO) or in the manufacturer's technical documentation.
Classification by slot type
Schlitz is the shape of the recess or profile on the bolt head, which determines the type of tool used to tighten it. Main types:
- Internal hexagon (Hex, Allen) – used in furniture and machine-building joints.
- External hexagon - the most common type, screwed with keys of the appropriate size.
- Torx (star-shaped) – has improved torque transmission, often used in the automotive industry.
- Pozidriv (PZ) – modification of the cross-shaped slot, which provides better grip with the screwdriver.
- Philips (PH) – standard cross-shaped slot, widely used in construction and electronics.
- Straight (Slotted, Flathead) - the simplest, used mainly in household fasteners.
- Square (Robertson) - square slot, popular in North America.
- Tri-Wing, Spanner, Torq-Set, One-Way – special types to protect against unauthorized untwisting.
Marking of bolts
As a rule, indetailed labeling is used that indicates their characteristics and standards. Consider an example of labeling:
Bolt DIN 933-8.8×M12×1.75-50.A.035
- Word "Bolt": Indicates the type of fastener.
- DIN standard: Indicates the standard to which the bolt is manufactured, for example "FROM 933».
- Strength class: It is indicated without a dot between the numbers, for example, "8.8", which indicates the mechanical properties of the product.
- Nominal diameter thread: Denoted by a number, for example, "M12", which indicates the diameter of the thread in millimeters.
- Step thread: It is indicated, for example, "1.75" mm, which indicates the pitch of the thread.
- Bolt length: Indicated by a number, for example "50" mm, indicating the total length of the product.
- Steel index: Indicates the use of annealed or automatic steel, for example "A" for automatic steel.
- Coating thickness: Denoted by a number, for example, "35" μm, which indicates the thickness of the applied protective layer.
This marking allows you to accurately identify hardware and its characteristics, ensuring compliance with design requirements and operating conditions.
Fasteners that meet certain standards of strength and construction are subject to mandatory marking.
This includes:
Bolts with a hexagonal head of strength classes 4.6, 5.6, 6.6, 8.8, 9.8, 10.9, 12.9.
Screws with a cylindrical head and a hexagonal recess under the key, as well as studs of strength classes 8.8, 9.8, 10.9, 12.9.
The most common designations of hardware sizes on drawings:
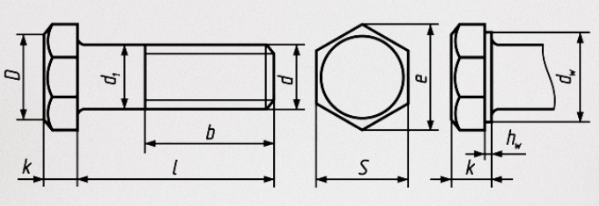
Fig. 5 Pdetermination of hardware sizes on drawings
d – nominal thread diameter;
d1 – the diameter of the smooth part of the rod;
dIn – diameter of the supporting surface of the head;
hIn – height of the supporting surface of the head;
k – head height;
P – threading step;
b – thread length of the nut end;
S - head width (key size);
e is the diameter of the circumscribed circle;
l is the length.
To measure the diameter, you can use a caliper, a micrometer or a template ruler.



 Bolts (20)
Bolts (20)