Metric thread (Fig. 5) is used mainly in screw connections of parts. Tight metric threads are used for fitting pins into product bodies and in other similar cases when it is necessary to eliminate the possibility of the pin being unscrewed when unscrewing the nut or its self-unscrewing without additional fasteners. Standards for metric threads provide thread elements with diameters up to 1 mm (0.25-0.9 mm) and over 1 mm (1-600 mm). The profile angle of metric threads is 60°.
he pitch of metric threads is measured in millimeters.
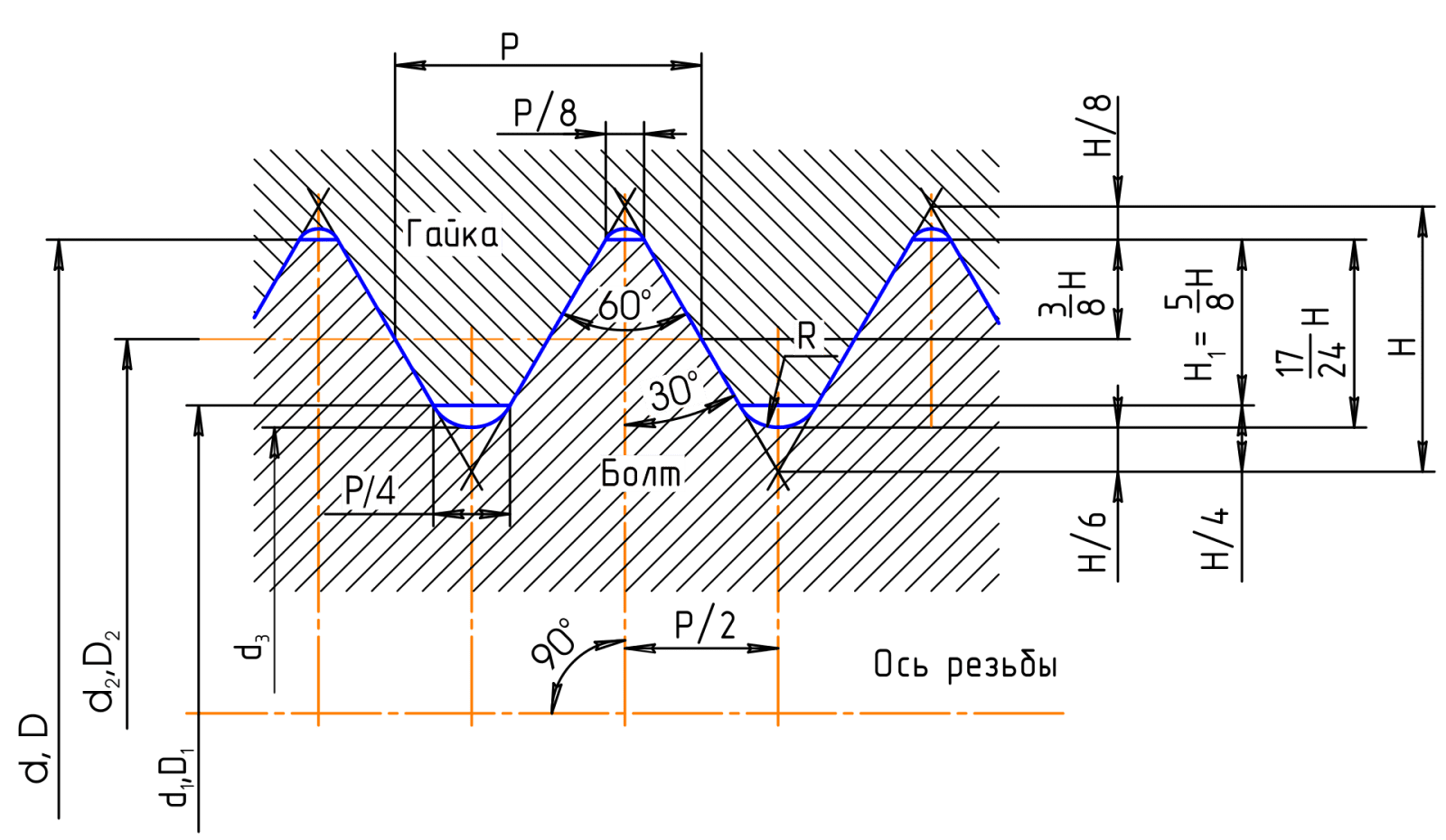
Fig. 5. Metric thread
MAIN THREAD PARAMETERS
Pitch (P) is the distance between the profile sides of the same name, measured in fractions of a meter, in fractions of an inch, or the number of threads per inch — it is the denominator of a common fraction, the numerator of which is an inch. It is expressed as a natural number (for example: 28, 19, 14, 11). Outer diameter (D, d), the diameter of the cylinder described around the tops of the outer (d) or hollows of the inner thread (D). Equal to the diameter of the bolt blank before thread cutting. Average diameter (D2, d2), the diameter of the cylinder, the product of which intersects the profile of the thread in such a way that its segments formed at the intersection with the groove are equal to half of the nominal pitch of the thread. Internal diameter (D1, d1), the diameter of the cylinder inscribed in the depressions of the external (d1) or top of the internal thread (D1). Equal to the diameter of the hole of the nut blank before thread cutting:
D1 = D−2×(H−2c)
Travel (Ph) is the distance along a line parallel to the axis of the thread between any starting midpoint on the side of the thread and the midpoint obtained when the starting midpoint is moved along the helical line by an angle of 360°, or — the value relative to the axial movement of the threaded part in one turn. In a single-step thread, the stroke is equal to a step, in a multi-step thread, the step P is created by the number of steps n:
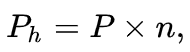
The height of the initial threading triangle (H).
Thread cut(s).
Cone angle of the conical thread (∅).
Thread elevation angle (ψ).
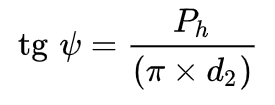
Standards for metric threads:
1. GOST 24705-2004 (ISO 724:1993) "Metric thread. Basic dimensions";
2. GOST 9150-2002 "Basic norms of interchangeability. The thread is metric. Profile";
3. GOST 8724-2002 "Basic norms of interchangeability. The thread is metric. Diameters and steps";
4. ISO 965-1:1998 “General purpose ISO metric threads. Tolerances Part 1. Principles and main characteristics";
5. ISO 965-2:1998 “ISO metric threads for general purposes. Tolerances Part 2. Limit dimensions of threads for bolts and nuts of general purpose. Average class of accuracy";
6. ISO 965-3:1998 “General purpose ISO metric threads. Tolerances Part 3. Deviations for structural threading";
7. ISO 965-4:1998 “ISO metric threads for general purposes. Tolerances Part 4: Limit dimensions for external hot-dip galvanized screw threads for assembly with internal screw threads tapped from tolerance position H or G after galvanization';
8. ISO 965-5:1998 “ISO metric threads for general purposes. Tolerances Part 5. Limit dimensions for internal screw threads of screws for assembly with external screw threads, hot-dip galvanized, with a maximum tolerance position size h before galvanization';
9. ISO 68-1 “General Purpose ISO Screw Threads. Basic profile. Metric threads";
10. ISO 261:1998 “ISO metric threads for general purposes. General appearance";
11. ISO 262:1998 “ISO metric general purpose threads. Selected dimensions for screws, bolts and nuts";
12. BS 3643 "ISO metric screw threads";
13. DIN 13-12-1988 "Metric ISO basic and precision threads with a diameter from 1 to 300 mm. Selection of diameters and steps";
14. ANSI B1.13m, ANSI B1.18m "M-Code Metric Threads with Profile Based on ISO 68".
Conventional designations in the thread marking: the letter M (metric), the numerical value of the nominal diameter of the thread (d, D on the diagram, the same as the outer diameter of the thread on the bolt) in mm, the numerical value of the pitch (for threads with a small pitch) (P on the diagram) and the letters LH for left-hand threads. For example, a thread with a nominal diameter of 16 mm with a large pitch is designated as M16; a thread with a nominal diameter of 36 with a small pitch of 1.5 mm — M36×1.5; the same diameter and pitch, but the left thread is M36?1.5LH. These parameters can be marked on the tool in different places and not have an M-code designation, so the numbers 36 and 1.5, marked in different places, indicate M36×1.5LH. Also, on Soviet and Russian instruments, the abbreviated marking of the fine step is often found, for example, 2М16 or 1М16, which means "М16, fine, second" or "М16, fine, first", respectively. In this case, 1M means the first step from the main one, 2M means the second. For this example, 1M16 means M16×1.75, and 2M16 means M16×1.5, since the basic pitch of M16 is 2 mm. The main steps of metric threading are presented in Tables 1 and 2.
Table 1. The main steps of a metric thread for diameters of 0.25-0.9 mm
| М0,25 | М0,3 | М0,35 | М0,4 | М0,45 | М0,5 | М0,55 | М0,6 | М0,7 | М0,8 | М0,9 |
| 0,075 | 0,08 | 0,09 | 0,1 | 0,1 | 0,125 | 0,125 | 0,15 | 0,175 | 0,2 | 0,225 |
Table 2. The main steps of a metric thread for diameters of 1-600 mm
| Thread diameter d=D | Step | Average | Internal | Working height of the thread profile | ||
| Number | carvings by R | diameter | diameter | H1 | ||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | d2=D2 | d1=D1 | ||
| 2 | 0,4 | 1,74 | 1,567 | 0,217 | ||
| 2,2 | 0,45 | 1,908 | 1,713 | 0,244 | ||
| 2,5 | 0,45 | 2,208 | 2,031 | 0,244 | ||
| 3 | 0,5 | 2,675 | 2,469 | 0,271 | ||
| 3,5 | 0,6 | 3,11 | 2,851 | 0,325 | ||
| 4 | 0,7 | 3,545 | 2,242 | 0,379 | ||
| 4,5 | 0,75 | 4,013 | 3,688 | 0,406 | ||
| 5 | 0,8 | 4,48 | 4,134 | 0,433 | ||
| 6 | 1 | 5,351 | 4,918 | 0,541 | ||
| 7 | 1 | 6,351 | 5,918 | 0,541 | ||
| 8 | 1,25 | 7,188 | 6,647 | 0,677 | ||
| 9 | 1,25 | 8,188 | 7,647 | 0,677 | ||
| 10 | 1,5 | 9,026 | 8,376 | 0,812 | ||
| 11 | 1,5 | 10,026 | 9,376 | 812 | ||
| 12 | 1,75 | 10,863 | 10,106 | 0,947 | ||
| 14 | 2 | 12,701 | 11,835 | 1,083 | ||
| 16 | 2 | 14,701 | 13,835 | 1,083 | ||
| 18 | 2,5 | 16,376 | 15,294 | 1,353 | ||
| 20 | 2,5 | 18,376 | 17,294 | 1,353 | ||
| 22 | 2,5 | 20,376 | 19,294 | 1,353 | ||
| 24 | 3 | 22,051 | 20,752 | 1,624 | ||
| 21 | 3 | 25,051 | 23,752 | 1,894 | ||
| 30 | 3,5 | 27,727 | 26,211 | 1,894 | ||
| 33 | 3,5 | 30,727 | 29,211 | 1,894 | ||
| 36 | 4 | 33,402 | 31,67 | 2,165 | ||
| 39 | 4 | 36,402 | 33,67 | 2,165 | ||
| 42 | 4,5 | 39,077 | 37,129 | 2,436 | ||
| 45 | 4,5 | 42,077 | 40,129 | 2,436 | ||
| 48 | 5 | 44,752 | 42,587 | 2,706 | ||
| 52 | 5 | 48,752 | 46,587 | 2,706 | ||
| 56 | 5,5 | 52,428 | 50,046 | 2,977 | ||
| 60 | 5,5 | 56,428 | 54,046 | 2,977 | ||
| 64 | 6 | 60,103 | 57,505 | 3,248 | ||
| 68 | 6 | 64,103 | 61,505 | 3,248 | ||

